Nitrox is a much-discussed topic among divers and underwater enthusiasts, but do you really know what makes it so special? This oxygen-enriched blend is revolutionizing the way we dive, offering significant advantages in terms of safety and dive duration. Whether you’re an experienced diver or just starting out, understanding the benefits of this gas can make a big difference in your underwater experience.
Ready to discover how it works and why more and more divers are choosing it? Keep reading to find all the answers to your questions!
Indice:

What is nitrox?
composed of nitrogen and oxygen. The unique aspect of Nitrox lies in its higher oxygen percentage compared to regular air, which contains 21% oxygen and 79% nitrogen. In the case of Nitrox, the oxygen percentage usually ranges between 28% and 40%, with the most common values being 32% and 36%.
Chemical composition
- Oxygen (O₂): between 28% and 40%, depending on the blend.
- Nitrogen (N₂): the remaining percentage, which decreases as oxygen increases.
This composition significantly alters the behavior of the mixture during a dive, reducing the amount of nitrogen absorbed by the body during bottom time.
What is the difference between nitrox and compressed air?
Standard compressed air used in most scuba dives is a balanced mixture of oxygen (21%) and nitrogen (79%) that remains unaltered in its natural composition. Nitrox, on the other hand, is an artificial mixture created by either adding oxygen or reducing the amount of nitrogen, achieved through specialized filling systems.

What is nitrox used for?
During a dive, the nitrogen in compressed air dissolves into the body tissues due to increased pressure. This phenomenon is the main reason behind no-decompression limits, which determine the maximum time a diver can stay at a given depth without requiring mandatory decompression stops during ascent.
With a Nitrox blend, the amount of nitrogen absorbed is reduced, which results in:
- Decreased risk of decompression sickness (DCS): the body accumulates less nitrogen, reducing the risks associated with its elimination.
- Extended no-decompression limits: you can stay underwater longer at intermediate depths compared to using compressed air.
- Improved post-dive comfort: reduced nitrogen absorption can minimize the feeling of fatigue often experienced after a dive.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of diving with nitrox?
Advantages
- Longer bottom time: with Nitrox, you can stay longer at certain depths compared to regular air, reducing no-decompression limits.
- Less post-dive fatigue: many divers report feeling less tired after using this gas.
- Reduced risk of decompression sickness: thanks to the lower nitrogen absorption.
Disadvantages
- Depth limitations: higher oxygen percentages require careful attention to oxygen toxicity, meaning you must adhere to shallower maximum depths compared to regular air.
- Cost and availability: using Nitrox requires specific equipment and certification, which can increase costs.
How long can a diver stay underwater with nitrox?
The duration of a dive with Nitrox depends on several factors, including the oxygen percentage in the mix, the depth reached, and the diver’s physiological limits. Nitrox allows for extended no-decompression dive times but requires careful planning to ensure safety.
No-decompression limits
The no-decompression limit (NDL) is the maximum time a diver can spend at a given depth without requiring mandatory decompression stops during ascent. With Nitrox, this limit increases compared to standard compressed air, as the reduced nitrogen in the mix means the body absorbs less nitrogen during the dive.
For example:
- With Compressed Air (21% Oxygen): at 30 meters, the no-decompression time is about 20 minutes.
- With Nitrox 32% (32% Oxygen): at 30 meters, the bottom time increases to about 30 minutes.
- With Nitrox 36% (36% Oxygen): at 30 meters, the bottom time can reach 40 minutes.
Note: these times are indicative and can vary depending on the dive computer used, the dive profile, and the diver’s physiology.
Safety limits: oxygen toxicity
One of the main constraints when using Nitrox is the partial pressure of oxygen (PPO₂). Excessive exposure to oxygen at high pressure can cause oxygen toxicity, a potentially life-threatening risk. Therefore, it’s essential to monitor the total oxygen exposure, known as %CNS (Central Nervous System Toxicity).
- Recreational diving with no or minimal decompression: PPO₂ should not exceed 1.4 bar during the dive.
- Technical diving with decompression and multiple gas mixtures: PPO₂ should not exceed 1.6 bar.
Practical example: diving with nitrox 32%
Let’s consider a dive with Nitrox 32% at a depth of 20 meters:
- Maximum operating depth (MOD): 33 meters.
- No-decompression limit: approximately 25 minutes.
This means that at 20 meters with Nitrox 32%, you can stay underwater longer than with compressed air while maintaining a wide safety margin. However, it’s crucial not to exceed the MOD and to respect the calculated limits.
Planning and necessary tools
To properly plan a dive with Nitrox, you’ll need:
- Knowledge of appropriate bottom times for nitrox use: to calculate new no-decompression limits.
- Specific dive training: certification for use it.
- Gas analyzer: to verify the gas mixture before the dive.
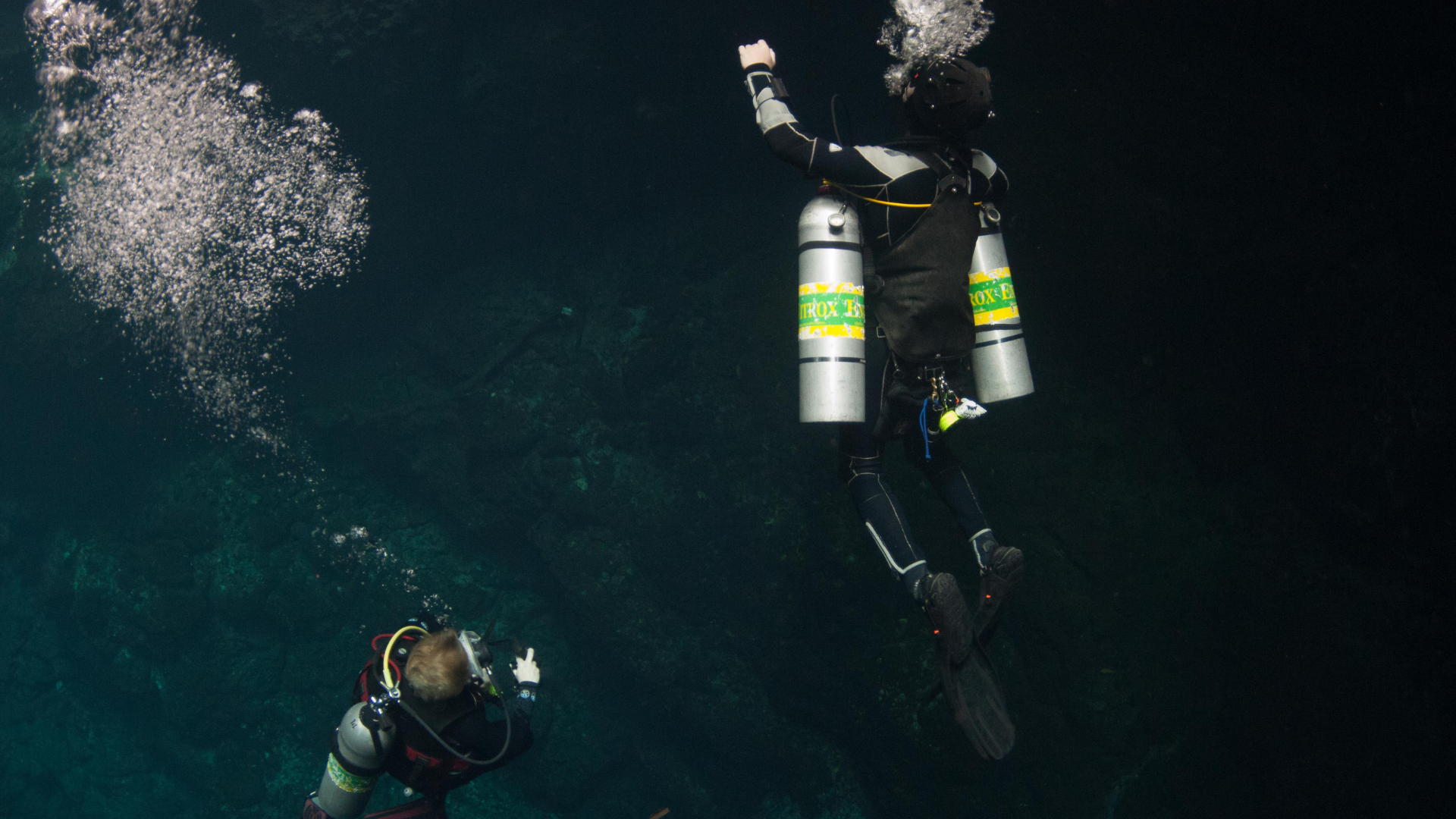

Nitrox diving: how deep can a diver go?
The maximum depth a diver can reach using Nitrox depends on the oxygen percentage in the mixture and the resulting partial pressure of oxygen (PPO₂). PPO₂ is a critical factor in ensuring dive safety, as excessive values can cause oxygen toxicity with severe symptoms like seizures or loss of consciousness.
What is the maximum operating depth (MOD)?
The MOD (Maximum Operating Depth) is the maximum depth at which a Nitrox mixture can be safely used. It is calculated to ensure that the PPO₂ does not exceed the safety limit, typically set at 1.4 bar for recreational dives. A higher limit of 1.6 bar may be acceptable in emergency situations but is not recommended for standard dives.
Formula for calculating MOD
The MOD is calculated using the following formula:
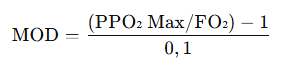
Where:
- PPO₂ Max is the maximum acceptable partial pressure (usually 1.4 bar).
- FO₂ is the fraction of oxygen in the mixture (e.g., 0.32 for Nitrox 32%).
Examples of maximum depths for common mixtures
| Nitrox mixture | Maximum operating depth (MOD) |
| Nitrox 32% | 33 meters |
| Nitrox 36% | 28 meters |
| Nitrox 40% | 25 meters |
Exceeding these depths increases the risk of oxygen toxicity, making it essential to use a dive computer or depth gauge and to constantly monitor depth during the dive.
Why does nitrox limit depth?
Increasing the oxygen content in the mixture reduces the nitrogen component but amplifies the risk of oxygen toxicity at higher pressures. This constraint makes this gas ideal for intermediate depths but unsuitable for technical dives below 40 meters.
For example:
- Nitrox 32% is optimal for dives between 15 and 30 meters, where it extends bottom times.
- Nitrox 36% is perfect for shallow dives, between 10 and 25 meters, offering significantly longer bottom times.
Is it worth getting nitrox certified?
Absolutely! Earning your Nitrox certification is an important step for any diver looking to enhance their underwater experience. Not only does it allow you to safely use it, but it also opens up opportunities to extend bottom times, reduce fatigue, and dive more safely during repetitive dives.
That’s why we offer a specialized course to help you obtain your certification.
What will you learn in the course?
A Nitrox specialty course provides both theoretical and practical knowledge to use this gas blend responsibly. Here are the key skills you will acquire:
- Nitrox theory: understanding the composition of this gas and its effects on the human body.
- Mix analysis and cylinder marking: how to use a gas analyzer to verify the oxygen percentage in your tank and mark it for easy identification.
- MOD and maximum bottom time calculation: learning how to determine the Maximum Operating Depth (MOD) for your blend and the maximum allowable bottom time.
- Dive planning: using Nitrox tables and dive computers to calculate no-decompression limits and monitor oxygen exposure (%CNS and OTU).
Who should take the nitrox course?
The course is ideal for:
- Recreational divers: looking to extend bottom times and minimize risks associated with nitrogen absorption.
- Underwater photographers: needing more time to capture photos or videos without pressure.
- Vacation divers: performing repetitive dives over short periods and wanting to feel fresher between dives.
- Technical divers: preparing for advanced dives and more complex gas mixtures.
Where to get nitrox certified?
In addition to the many city clubs, Argentario Divers offers a specialized course that combines theory, practice, and technical skills. Here’s what we provide:
- Experienced and qualified instructors.
- State-of-the-art equipment, including gas analyzers and dive computers.
- Comprehensive training to prepare you for safe Nitrox use and to maximize its benefits.
-

Nitrox Diving
€ 225,00 – € 261,00Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product pageOxygen-enriched air, also known as nitrox or EANx, contains less nitrogen than normal air. Discover all the benefits.
Course duration: 1 day
Find us here
Lungomare Andrea Doria, 103
58019 – Porto Ercole Monte Argentario (GR)
Diving with Nitrox is a game-changer for anyone looking to enhance their scuba experience. With this gas blend, you can extend bottom times, reduce the risk of decompression sickness, and feel less fatigued after dives. However, to make the most of its benefits, acquiring specific skills through certification is essential.
The Argentario Divers Nitrox Specialty Course is the perfect choice for anyone who wants to learn how to use it safely, with the guidance of expert instructors and cutting-edge equipment.
Don’t let the limits of compressed air hold you back. Sign up for our course today and discover a new way to dive—longer, safer, and more rewarding.



